GAO-21-104622
Published: Sep 09, 2021
Publicly Released: Sep 09, 2021
What GAO Found
Exposure notification applications (apps)—which determine the proximity of users and notify people who have been in close contact with another user who was likely infectious—are expected to enhance the speed and reach of contact tracing and help slow the spread of infectious diseases such as COVID-19. As of June 2021, almost half (26/56) of U.S. states, territories, and the District of Columbia had deployed an app for COVID-19, all using a system developed jointly by Google and Apple (see figure). In the absence of a national app, states independently launched apps, resulting in a staggered rollout over 10 months beginning in August 2020.
Map of deployment of exposure notification apps by U.S. states and territories, as of June 2021
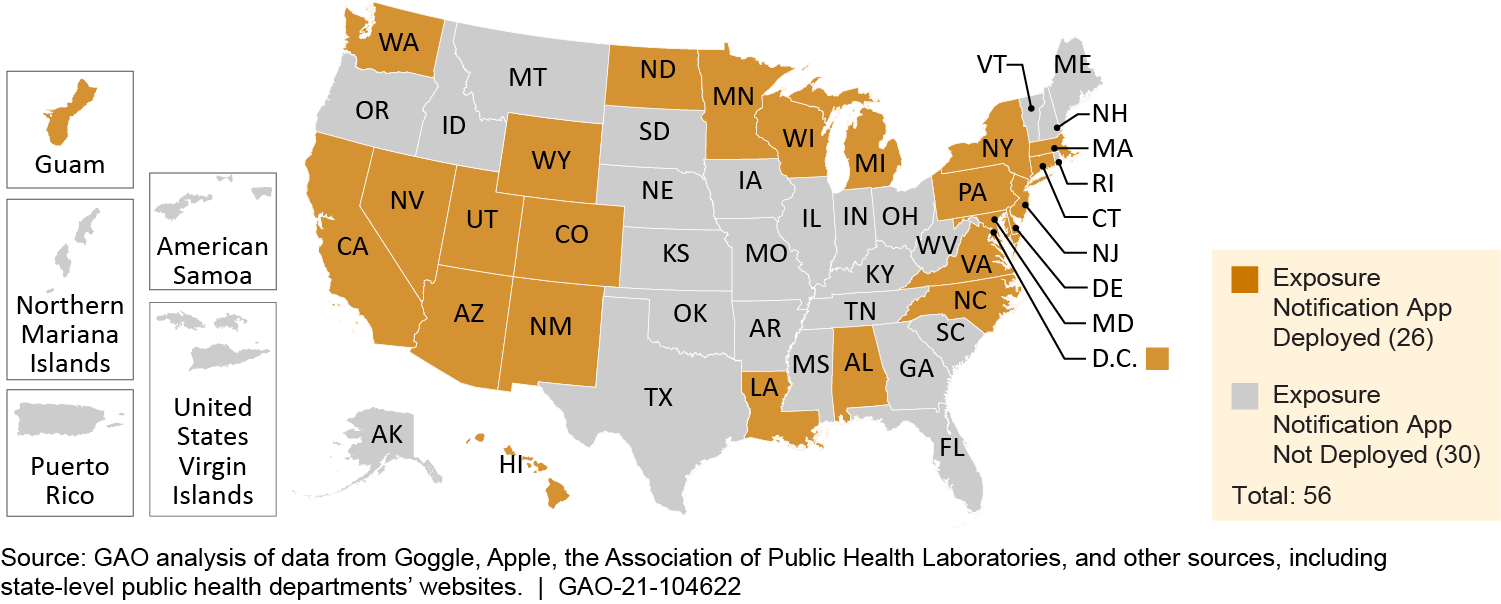
Reported app development costs for selected states varied, ranging from no cost (provided by a nonprofit organization) to $700,000. Marketing costs for selected states ranged from $380,000 to $3.2 million. Reported app download levels in the selected states ranged from 200,000 to more than 2 million, as of June 2021.
GAO identified several challenges limiting app use and the ability of states and others to determine whether the apps were effective…